Periodontal diseases range from simple gum inflammation to serious disease that results in major damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth. In the worst cases, teeth are lost. Whether your gum disease is stopped, slowed, or gets worse depends a great deal on how well you care for your teeth and gums every day, from this point forward.
What causes gum disease?
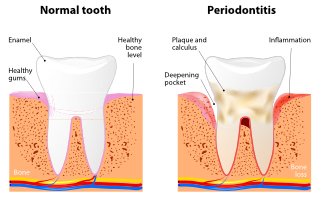
Our mouths are full of bacteria. These bacteria, along with mucus and other particles, constantly form a sticky, colorless “plaque” on teeth. Brushing and flossing help get rid of plaque. Plaque that is not removed can harden and form “tartar” that brushing doesn’t clean. Only a professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist can remove tartar.
Gingivitis
The longer plaque and tartar are on teeth, the more harmful they become. The bacteria cause inflammation of the gums that is called “gingivitis.” In gingivitis, the gums become red, swollen and can bleed easily. Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that can usually be reversed with daily brushing and flossing, and regular cleaning by our hygienist. This form of gum disease does not include any loss of bone and tissue that hold teeth in place.
Periodontitis
When gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to “periodontitis” (which means “inflammation around the tooth”). In periodontitis, gums pull away from the teeth and form spaces (called “pockets”) that become infected. The body’s immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line. Bacterial toxins and the body’s natural response to infection start to break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. If not treated, the bones, gums, and tissue that support the teeth are destroyed. The teeth may eventually become loose and have to be removed.
How do I know if I have gum disease?
Symptoms of gum disease include:
- Bad breath that won’t go away
- Red or swollen gums
- Tender or bleeding gums
- Painful chewing
- Loose teeth
- Sensitive teeth
- Receding gums or longer appearing teeth
Any of these symptoms may be a sign of a serious problem, which should be checked as soon as possible.
How is gum disease treated?
The main goal of treatment is to control the infection. The number and types of treatment will vary, depending on the extent of the gum disease. Any type of treatment requires that the patient keep up good daily care at home. We may also suggest changing certain behaviors, such as quitting smoking, as a way to improve treatment outcome.
Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
In this process we remove the plaque through a deep-cleaning method called scaling and root planing. Scaling means scraping off the tartar from above and below the gum line. Root planing gets rid of rough spots on the tooth root where the germs gather, and helps remove bacteria that contribute to the disease.